Invoke AWS Lambda from AWS Step Functions with Terraform

Terraform
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool. It allows building, changing, and versioning the infrastructure. Terraform uses a declarative approach to define the infrastructure. Users will define the end infrastructure that they want and terraform will do the rest of the thing to have that infrastructure.
Terraform allows its users to define and describe the infrastructure using a declarative configuration language known as HCL or HashiCorp Configuration Language. When the end infrastructure is defined terraform will do the plan and then executes this plan to provision that infrastructure.
Terraform supports all the public clouds like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform aw well as private clouds such as VMWare vSphere, CloudStack, or OpenStack.
In this article, we will define an infrastructure for the AWS provider which will have an AWS Lambda and AWS Step Functions working together.
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a Function-as-a-Service platform by Amazon Web Services. It can run code without provisioning the servers. This allows the developers to focus only on code as AWS Lambda is taking care of everything else.
There are three core components of AWS Lambda. The handler function is the main function that will be run when lambda executes. Event Object is the first argument passed to the function when it gets executed. It contains information about the event invoking the lambda. And the Context Object contains lambda runtime information.
So let’s define our handler function for the lambda. For that create a folder lambda and inside that folder create a file handler.py. The code for the handler function will be as below.
import logging
LOGGER = logging.getLogger()
LOGGER.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def handler(event, context):
LOGGER.info(f'Event Object: {event}')
LOGGER.info(f'Context Object: {context}')
event['key'] = 'value'
return event
This is a super simple function. In the function, we are logging the event object and context object and set value as the value of the key key in the event object. Finally, we are returning the updated event object.
Now let’s write some terraform code for this lambda function. For that create a folder terraform and inside that folder create a file lambda.tf. The content of this file will be as follows.
// Lambda function
resource "aws_lambda_function" "lambda_function" {
function_name = var.lambda_function_name
filename = data.archive_file.lambda_zip_file.output_path
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_zip_file.output_base64sha256
handler = "handler.handler"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_assume_role.arn
runtime = "python3.8"
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
}
// Zip of lambda handler
data "archive_file" "lambda_zip_file" {
output_path = "${path.module}/lambda_zip/lambda.zip"
source_dir = "${path.module}/../lambda"
excludes = ["__init__.py", "*.pyc"]
type = "zip"
}
// Lambda IAM assume role
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_assume_role" {
name = "${var.lambda_function_name}-assume-role"
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.lambda_assume_role_policy_document.json
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
}
// IAM policy document for lambda assume role
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "lambda_assume_role_policy_document" {
version = "2012-10-17"
statement {
sid = "LambdaAssumeRole"
effect = "Allow"
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole"]
principals {
identifiers = ["lambda.amazonaws.com"]
type = "Service"
}
}
}
Here we are creating two resources aws_lambda_function and aws_iam_role. The lambda function that we defined earlier is being zipped in archive_file and it is also being referred to in aws_lambda_function resource. We are creating aws_iam_role resources as lambda requires it to run the function. The policy document of this resource is defined in aws_iam_policy_document the data object.
One important thing to note here is that we are taking the name of the lambda function from var.lambda_function_name. Terraform allows us to define some variables and use them in the terraform files. So let’s create a file vars.tf that will contain all of our variables. For now, it contains only the following.
variable "lambda_function_name" {
description = "The name of the lambda function."
type = string
default = "test_lambda"
}
And at this point, the directory structure will be as below.
.
+-- lambda
| +-- handler.py
+-- terraform
| +-- lambda.tf
| +-- vars.tf
AWS Step Functions
AWS Step Functions is the orchestration of serverless microservice architecture. It divides a complex business workflow into smaller steps and implements them in AWS Lambda or other AWS services. The main building blocks of AWS Step Functions are the states. There are several types of state like Task, Pass, Choice, Wait, Parallel, Map, Fail, and Succeed. The states are defined in AWS States Language which is a JSON-based specification language. AWS Step Functions execute the states according to the order in which they are defined and retry them if any error or exception occurs.
Now that we know what AWS Step Functions actually is, it’s time to define a step function in terraform which will invoke the lambda that we have defined earlier. For that create a file step_function.tf inside the terraform folder and put the below code in that file.
resource "aws_sfn_state_machine" "sfn_state_machine" {
name = var.step_function_name
role_arn = aws_iam_role.step_function_role.arn
definition = <<EOF
{
"Comment": "Invoke AWS Lambda from AWS Step Functions with Terraform",
"StartAt": "HelloWorld",
"States": {
"HelloWorld": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.arn}",
"End": true
}
}
}
EOF
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "step_function_role" {
name = "${var.step_function_name}-role"
assume_role_policy = <<-EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"Service": "states.amazonaws.com"
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": "StepFunctionAssumeRole"
}
]
}
EOF
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "step_function_policy" {
name = "${var.step_function_name}-policy"
role = aws_iam_role.step_function_role.id
policy = <<-EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"lambda:InvokeFunction"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "${aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.arn}"
}
]
}
EOF
}
Here we are creating a resource aws_sfn_state_machine which is the step function and aws_iam_role which is the role that will be used by the step function.
This step function has only one state HelloWorld which is a Task type. We have set the Resource of the HelloWorld state to the ARN of the lambda function using this ${aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.arn}.
Once again we are taking the name of the step function from the terraform variable. So add the following terraform code to vars.tf.
variable "step_function_name" {
description = "The name of the step function."
type = string
default = "test_step_function"
}
Deploy
Now that we have defined the infrastructure for an AWS Lambda and an AWS Step Functions in terraform, it is time to deploy and test them. For this reason, create a file main.tf inside terraform folder and put the below code there.
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
profile = "default"
}
Here we are specifying the provider as aws and passing the region and profile. So finally the directory structure will be as below.
.
+-- lambda
| +-- handler.py
+-- terraform
| +-- lambda.tf
| +-- main.tf
| +-- step_function.tf
| +-- vars.tf
At this point we are ready to go, so open up the terminal and run the following commands in it.
>>> terraform init # it will perform initialization step
>>> terraform plan # see the execution plan of terraform
>>> terraform apply # apply the infrastructure in AWS
After performing those commands login to your AWS Step Functions console and start the execution of the step function (“which you just deployed”) by clicking the Start Execution button.
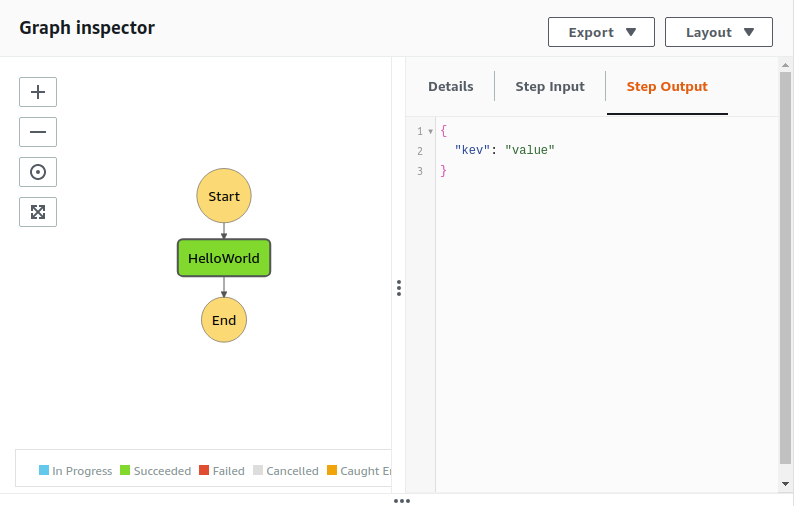
As it is a simple step function, so it will get executed immediately. And you can see the key-value pair that we have set in the lambda handler is showing in the output of the step function.
The complete code of this article can be found in this repository.